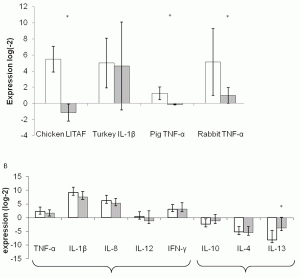
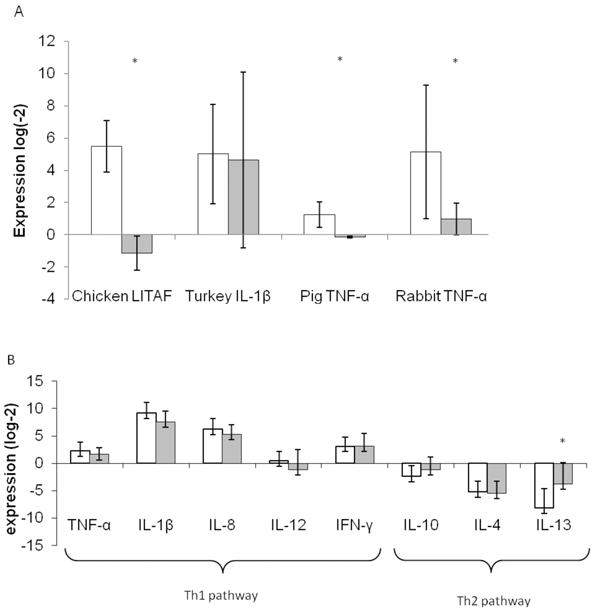
Ex-vivo LPS stimulation model coupled with quantitative PCR and its multispecies application in immunonutrition
22 February 2010 | By
Disorders of the immune systems leading to chronic inflammation and allergies are increasing in modern societies. While the possible causative factors are both environmental and nutritional, prevention and even curative options may be derived from our diet. Because background levels of cytokine expression in the general population are generally low,…