Merck’s ISENTRESS® (raltegravir) in combination therapy demonstrated efficacy in a Phase II Study
Posted: 18 July 2011 | | No comments yet
Extending to nearly five years in previously untreated adults with HIV-1…


Merck (NYSE: MRK), known as MSD outside the United States and Canada, today announced final results from a Phase II clinical study, extending out to 240 weeks, of its integrase inhibitor ISENTRESS® (raltegravir) Tablets in combination therapy in previously untreated (treatment-naïve) adult HIV-1-infected patients. The regimen containing ISENTRESS showed efficacy similar to the regimen containing efavirenz at suppressing HIV-1 viral load to undetectable levels (less than 50 copies/mL) and at improving CD4 counts in treatment-naïve adult patients. Data also showed that ISENTRESS in combination therapy resulted in fewer reported drug-related adverse events (AEs) than efavirenz, and showed a modest impact on low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol and triglycerides. These 240-week results will be presented on July 20th at the 6th International AIDS Society (IAS) Conference on HIV Pathogenesis, Treatment and Prevention in Rome.
“In this Phase II study, ISENTRESS demonstrated comparable efficacy and tolerability to efavirenz at 240 weeks in treatment-naïve adult patients with HIV-1,” said primary investigator Dr. Eduardo Gotuzzo, professor of medicine, infectious diseases and tropical medicine, Universidad Peruana Cayetano Heredia, Lima, Peru, who presented the data. “Because physicians consider many factors when selecting antiretroviral therapy for adult HIV-1 patients new to treatment, the results seen in this Phase II study with ISENTRESS in combination therapy showing a modest impact on LDL and triglycerides provide important insights.”
ISENTRESS is indicated in combination with other antiretroviral (ARV) agents for the treatment of HIV-1 infection in treatment-naïve and treatment-experienced adults. The label for ISENTRESS is based on analyses of plasma HIV-1 RNA levels through 96 weeks in three double-blind controlled Phase III clinical studies of ISENTRESS. Two of these studies were conducted in clinically advanced, three-class ARV [non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor (NNRTI), nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor (NRTI), protease inhibitor (PI)] treatment-experienced adults and one was conducted in treatment-naïve adults. The safety and efficacy of ISENTRESS have not been established in pediatric patients. The use of other active agents with ISENTRESS is associated with a greater likelihood of treatment response.
Protocol 004 study design
In this completed multicenter, double-blind, randomized, active-controlled Phase II study, 198 previously untreated HIV-1-infected adult patients received either 400 mg ISENTRESS orally twice daily (n=160) or 600 mg efavirenz orally once daily (n=38), each in combination with tenofovir/lamivudine (TDF/3TC), beginning at week 48. During the first 48 weeks of the study, patients receiving ISENTRESS were randomized to one of four dose regimens (100, 200, 400 and 600 mg twice daily). After which, all patients taking a regimen including ISENTRESS received the 400 mg dose twice daily. The study’s primary endpoints were reductions in HIV-1 viral load to less than 50 copies/mL and an evaluation of safety and tolerability. Secondary endpoints included ARV activity as measured by the proportion of patients achieving HIV-1 viral load to less than 400 copies/mL and change from baseline in CD4 cell count at week 240. The evaluation of total cholesterol, LDL cholesterol and triglycerides were exploratory analyses.
The data reported at IAS 2011 represent final 240-week results from this Phase II trial.
Patients who entered the study were required to have HIV-1 viral loads greater than 5,000 copies/mL. At baseline, the geometric mean HIV-1 viral load level for patients on the regimen including ISENTRESS was 55,266 copies/mL (n=160) and 67,554 copies/mL (n=38) for the regimen with efavirenz. Mean baseline CD4 cell counts were 305 cells/mm3 and 280 cells/mm3 for the groups receiving ISENTRESS and efavirenz, respectively.
ISENTRESS in combination therapy maintained viral load suppression and increased CD4 cell counts at 240 weeks of treatment in previously untreated adult patients with HIV-1
At week 240 of this study, the regimen containing ISENTRESS suppressed HIV-1 viral load levels to below 50 copies/mL in 68.8 percent of patients compared to 63.2 percent of patients on the regimen containing efavirenz (95 percent CI).
Additionally, 71.9 percent of patients on the regimen containing ISENTRESS and 65.8 percent of patients on the regimen containing efavirenz maintained HIV-1 viral load suppression below 400 copies/mL (95 percent CI).
Patients on the regimen containing ISENTRESS experienced an increase from baseline in mean CD4 cell count of 301.7 cells/mm3 compared to 275.6 cells/mm3 for patients on the regimen containing efavirenz.
Tolerability profile
Cumulative rates of drug-related clinical AEs at 240 weeks were lower in the regimen containing ISENTRESS versus the regimen containing efavirenz (55 percent vs. 76 percent, respectively).
Additionally, the most commonly reported AEs from the study in the regimens containing ISENTRESS and efavirenz, respectively, were diarrhea (6.9 percent vs. 10.5 percent), nausea (12.5 vs. 10.5 percent), dizziness (8.1 vs. 26.3 percent), headache (8.8 vs. 23.7 percent), abnormal dreams (6.9 percent vs. 18.4 percent), insomnia (8.1 percent vs. 13.2 percent) and nightmares (0.0 percent vs. 10.5 percent).
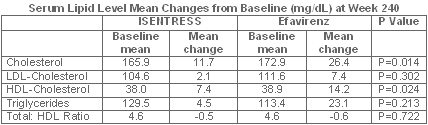
Exploratory analyses on lipids
Exploratory analyses in this Phase II study included the change in serum lipids.

Additional ISENTRESS data presented at IAS 2011
Poster presentations
- Impact of Treatment Failure with Three Traditional Antiretroviral (ARV) Classes of Drugs on Healthcare Resource Utilisation in Latin America (INFORM-LA study) (MOPE 222)
- Exploratory Analysis in the BENCHMRK Studies at Wk 192: Late Outcomes Based on Early Virologic Responses (MOPE 225)
In addition, 12 studies evaluating ISENTRESS clinical data from the Merck Investigator Studies Program (MISP) were presented at the conference.




