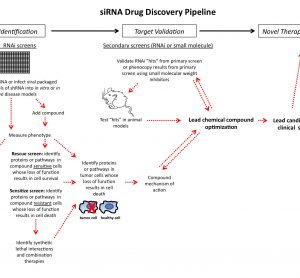
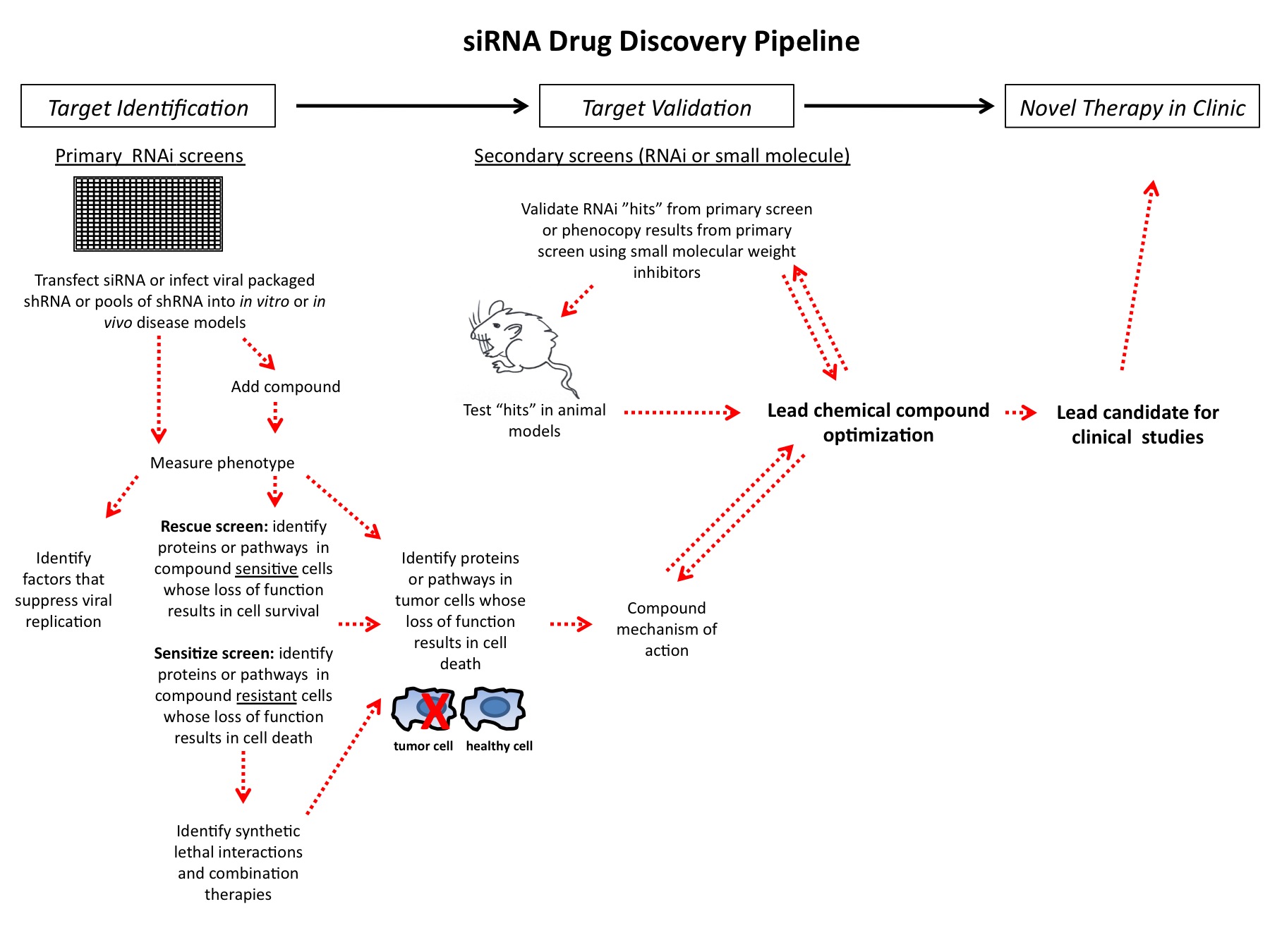
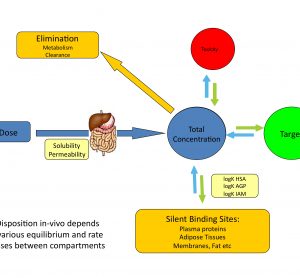
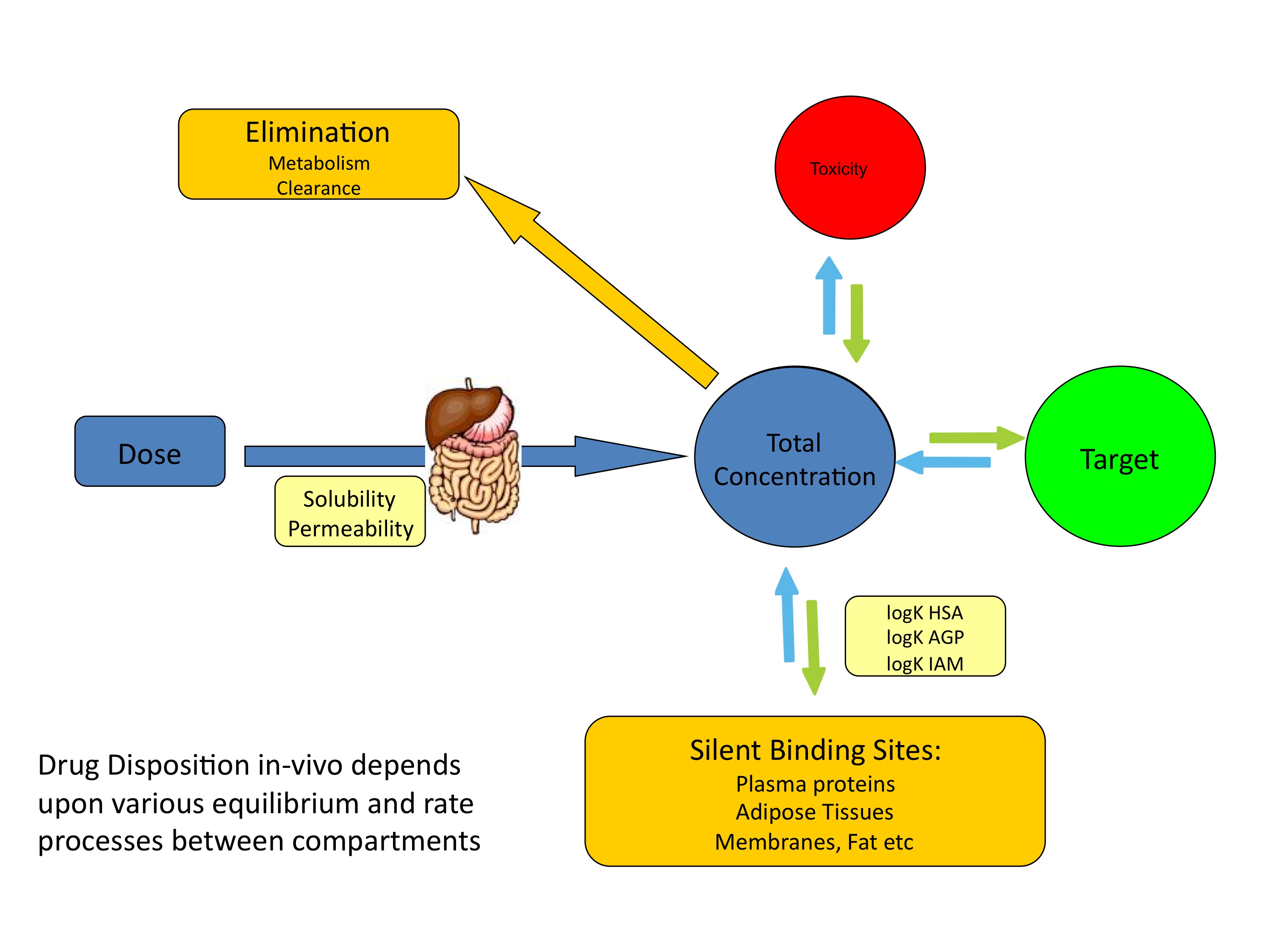
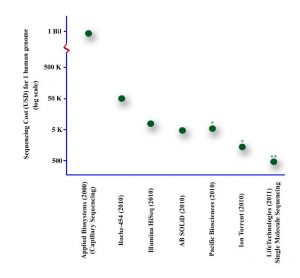
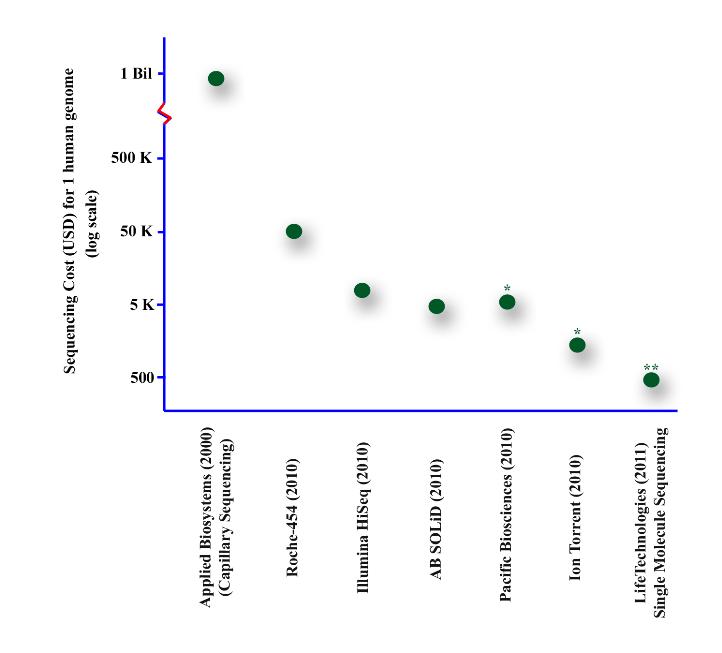
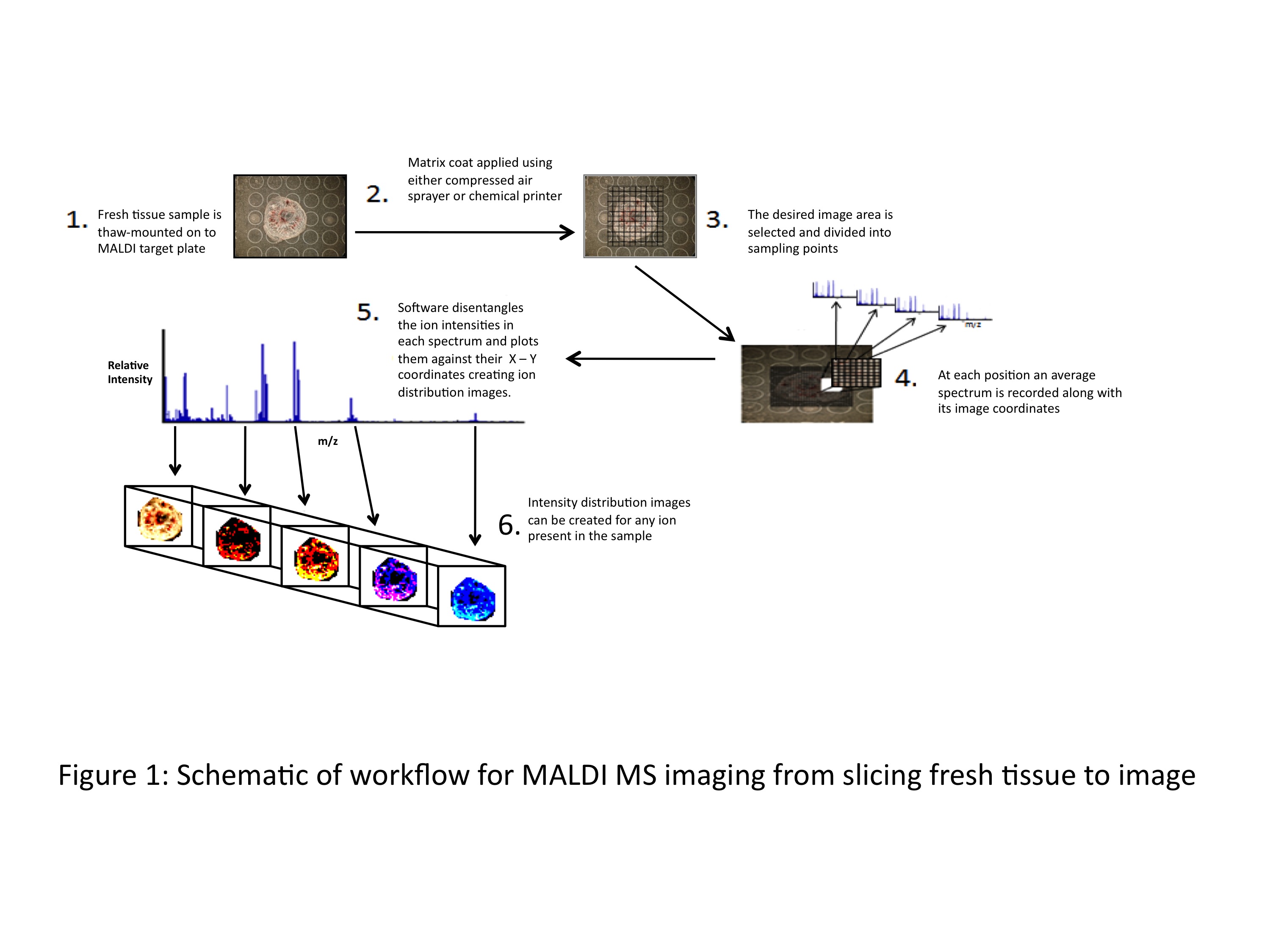
Article 5: The implementation of rapid microbiological methods
1 November 2010 | By Michael J. Miller, President, Microbiology Consultants, LLC
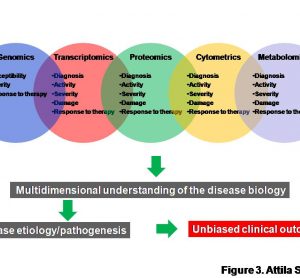
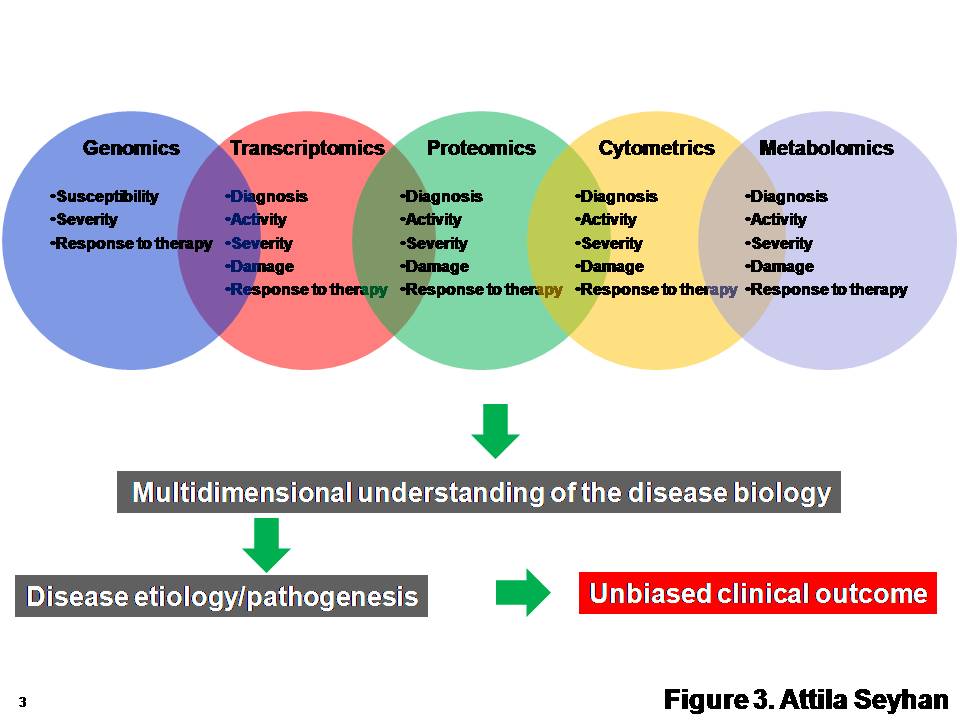
This is the fifth in a series of articles on rapid microbiological methods that will appear in European Pharmaceutical Review during 2010. In my previous four articles, I have provided an overview of the benefits of rapid microbiological methods (RMMs) as compared with conventional methods, validation strategies and regulatory perspectives…