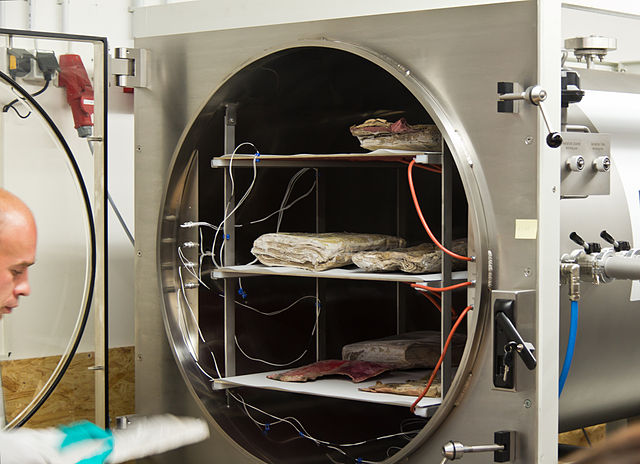
Lyophilization: cycle robustness and process tolerances, transfer and scale up
19 June 2008 | By Serguei Tchessalov and Nicholas Warne, Wyeth BioPharma, Andover
During the past 10-15 years, close attention has been paid to the development of optimal lyophilization cycles for different types of pharmaceuticals1-4. Recent advances in process control, such as the Smart Freeze-DryerTM technology or similar approaches, [5-7] make cycle development a routine procedure. The attention of many researchers has shifted…