Novel excipients for solubility enhancement
Posted: 16 February 2022 | Joey Glassco (Lubrizol Life Science Health), Nick DiFranco (Lubrizol Life Science Health) | No comments yet
Lubrizol Life Science Health colleagues Nick DiFranco, Global Market Segment Manager for Oral Treatments, and Joey Glassco, Senior Global Market Manager for Parenteral Drug Delivery, explore the use of amorphous solid dispersions and polymeric micelles for solubility enhancement.


Between 40 and 70 percent of marketed drugs and up to 90 percent of all new chemical entities (NCEs) registered suffer from poor water solubility. This can have significant negative consequences for the bioavailability of the active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) and potentially impact its therapeutic effect.
The Biopharmaceutical Classification System (BCS) is widely used across the pharmaceutical industry to classify APIs based on their solubility and permeability. It divides molecules into four separate classes according to their behaviour when interacting with water.
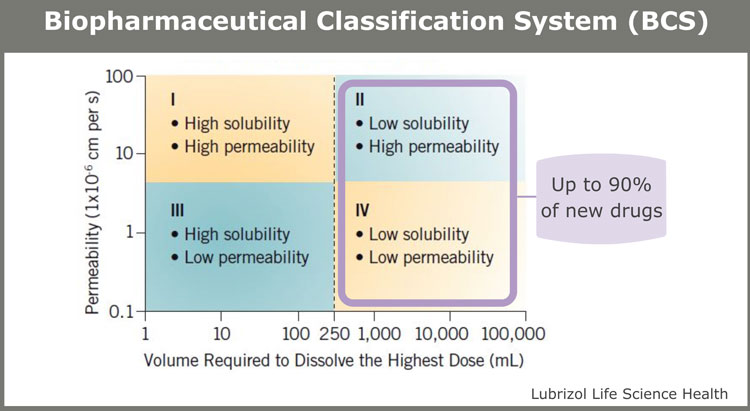

Figure 1
BCS Class II and IV molecules are particularly challenging when it comes to drug formulation, as they require solubility and/or permeability enhancement to provide therapeutic effect.
Different techniques to overcome solubility challenges
Various techniques can be used to help overcome drug solubility issues, depending on the unique characteristics of the API in question, as well as the specifics of the formulation and dosage form. These include the following:
- API chemical modification
- Encapsulation
- Inclusion complexes
- API physical modification and dispersion.
A number of these formulation techniques for poorly soluble drugs are facilitated by excipients. In this article, we will explore the use of amorphous solid dispersions and polymeric micelles for solubility enhancement.
Excipients in action
Amorphous solid dispersions (ASDs) or micellar solubilisation have been used for decades as pharmaceutical solubility and bioavailability enhancement tools (see Table 1). These techniques enhance the solubility of hydrophobic APIs by maintaining drug particles in an amorphous state (ie, ASDs) or solubilising the API in the micellar structure, respectively.
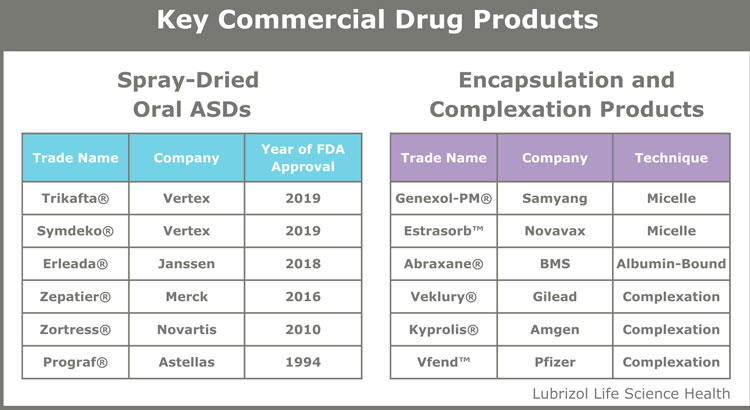

Table 1: Commercial drug products utilising solubility enhancement.
Approach #1: Amorphous solid dispersions
Preparation methods to form ASDs include hot-melt extrusion and solvent evaporation processes, such as spray drying.
Pharmaceutical spray drying is a continuous process wherein a liquid feed of API, polymer and solvent is atomised, dried and collected as solid particles.
When selecting excipient(s) for spray drying, there are several factors to consider, including solubility in common pharmaceutical solvents, the viscosity of the polymer in solution, and the ability to stabilise a large amount of drug in an amorphous form.
Apinovex™ polymers: Enabling highly efficient amorphous solid dispersions
Lubrizol’s Apinovex™ polymers are high molecular weight polyacrylic acid excipients designed to provide both processing and formulation benefits for spray-dried amorphous solid dispersions. Apinovex polymers enable formulators to enhance the solubility of BCS Class II and IV APIs and develop more efficient oral dosage forms.
The formulation benefits of Apinovex polymers include:
- High drug loading (up to 80 percent) via spray drying
- Significantly improved dissolution compared to crystalline API
- Stable amorphous solid dispersions even after six months at accelerated conditions
- Enables IP protection and lifecycle management/505(b)(2) formulations
- High glass transition temperature ensures stability of the ASD.
The processing benefits of Apinovex polymers include:
- Designed for standard spray drying and solvent-based processing techniques
- Soluble in water and common pharmaceutical solvents
- Produces low viscosity solutions for ease of processing.
Apinovex polymers are safe and compatible with a wide range of APIs. The polymer has been commercially manufactured according to IPEC-GMP guidelines and samples are available.
Approach #2: Polymeric micelle-based injectable formulations
Poor solubility is also a major barrier for injectable formulations. Micelles have been used in multiple commercial drug products to encapsulate and solubilise APIs for injection.
Amphiphilic block copolymers, which have a hydrophilic head and a hydrophobic tail, possess the ability to self-assemble and generate micellar structures offering solubilisation properties. Polymeric micelles also have a better safety profile compared with small molecule surfactants.
Apisolex™ polymers: Increase solubility up to 50,000x where others fail
The Apisolex polymer is a versatile, efficient and safe excipient technology employing a poly(amino acid) architecture to overcome the pitfalls of existing technologies. Apisolex technology enjoys robust patent protection, both in the US and internationally, which allows for applications with new chemical entities and drug products entering the market via the US Food and Drug Administration’s (FDA’s) 505(b)(2) regulatory pathway.
Both amorphous and highly crystalline hydrophobic APIs can be formulated using Apisolex technology. It decreases the amount of excipient required to solubilise a hydrophobic API compared to alternative excipients on the market, including Captisol® and other cyclodextrins, enabling the efficient development of next-generation parenteral products.
The Apisolex excipient’s poly (amino acid) amphiphilic architecture is composed of building blocks that naturally occur in the body, which results in a non-toxic, non-immunogenic, biocompatible and biodegradable alternative to PEG and other common solubility enhancers. The excipient is made according to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMPs) and is ready for use in clinical and commercial drug product manufacturing.
Apisolex technology is an ideal option for parenteral drug development projects where traditional excipients or other formulation techniques have failed or where a patent-protected technology is desired.
Request a sample today
LLS Health is dedicated to ensuring there are effective and reliable excipients available to address solubility issues in oral and injectable formulations. If you are looking for solubility enhancement options, contact our team below:
Request an oral-grade Apinovex™ polymer sample
Request an injectable-grade Apisolex™ polymer sample
Related topics
Active Pharmaceutical Ingredient (API), Drug Development, Drug Manufacturing, Excipients, Formulation
Related organisations
Lubrizol Life Science Health, US Food and Drug Administration (FDA)