Non-chemotherapy lymphoma treatment may provide durable remission
Posted: 19 June 2024 | Catherine Eckford (European Pharmaceutical Review) | No comments yet
Fifty four percent of evaluable patients with DLBCL attained a substantial tumour reduction with the five-drug regimen, trial data shows.

A non-chemotherapy multi-drug therapy enabled complete remission in 38 percent of evaluable patients with aggressive B-cell lymphoma, a Phase Ib/II clinical trial shows. This was observed in individuals who had experienced a return of their cancer or who were unresponsive to standard treatments.
Venetoclax, ibrutinib, prednisone, obinutuzumab, and lenalidomide (ViPOR) were used together in a treatment regimen in 50 patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL). Participants were given six cycles of the ViPOR combination.
There were 38 percent of those participants who achieved complete response. At two years post-treatment, 36 percent of all patients were alive. Furthermore, 34 percent of patients were reported as disease-free, the findings revealed.
“Many of these patients who stopped responding to standard treatments would have otherwise died within a year, and now we have a good proportion who are still alive past two years, and some past four years”
The National Institutes of Health (NIH) researchers highlighted that response varied by DLBCL subtype. Complete responses were seen mainly in two subtypes, including 62 percent of those with non-GCB DLBCL and 53 percent of people with high-grade B-cell lymphoma “double hit.”
Strengthening treatment effectiveness against DLBCL tumours
“Many of these patients who stopped responding to standard treatments would have otherwise died within a year, and now we have a good proportion who are still alive past two years, and some past four years,” shared Dr Christopher Melani, NCI’s Center for Cancer Research, who co-led the study. “It’s gratifying to see these long-term remissions and potential cures in patients.”
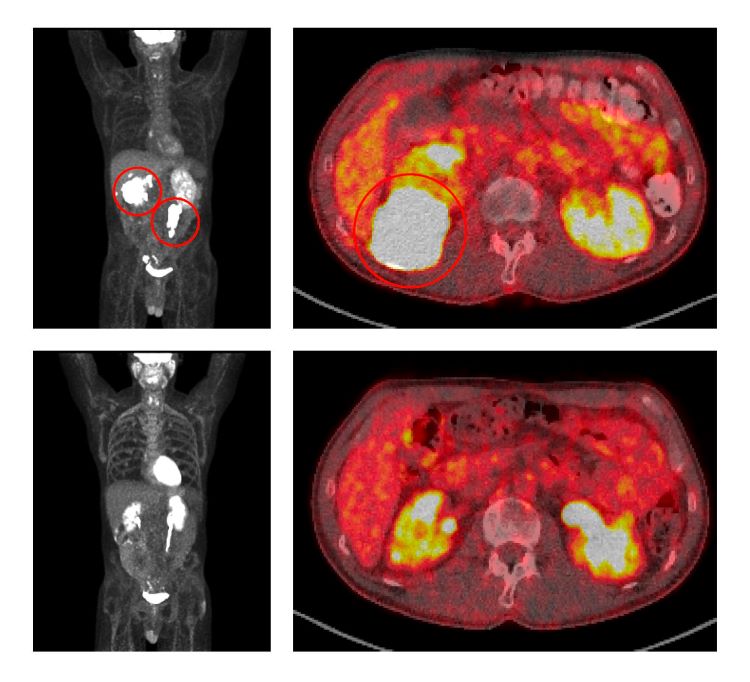

Before treatment with ViPOR, full-body and cross-sectional PET scans of a patient show large lymphoma tumours (circled in the top two panels). Following treatment, the tumours have disappeared (bottom two panels).
Credit: Center for Cancer Research/National Cancer Institute.
“By putting five drugs together, we believe that there will be some drug combination—either two, three, or more drugs—that will be particularly effective against that patient’s tumour,” Dr Melani remarked.
Side effects of ViPOR were reported to be “generally mild to moderate when compared with those of standard treatments”. These improved during the treatment breaks, the study found.
The researchers plan to conduct a larger Phase II study to establish the activity of ViPOR in people with non-GCB DLBCL and double-hit GCB DLBCL, they confirmed.
Data from the trial is published in the New England Journal of Medicine on 20 June.
Related topics
Anti-Cancer Therapeutics, Clinical Development, Clinical Trials, Data Analysis, Dosage, Drug Safety, Research & Development (R&D), Therapeutics
Related organisations
Related drugs
Imbruvica, lenalidomide, obinutuzumab, prednisone, venetoclax